Individual taxation
General Information
Income tax is charged on income derived by a resident natural person during a period of taxation from all sources of income in Estonia and outside Estonia. The taxable income of a natural person does not include fringe benefits, gifts and donations, dividends or other profit distributions subject to taxation at the level of a company.
Taxable persons
A natural person is a resident if his or her place of residence is in Estonia or if he or she stays in Estonia for at least 183 days over the course of a period of 12 consecutive calendar months. A person shall be deemed to be a resident as of the date of his or her arrival in Estonia.
Residence
If the residency prescribed on the basis of a tax treaty differs from the residency prescribed pursuant to law or if the tax treaty prescribes more favourable conditions for taxation of income than those provided by law, the provisions of the tax treaty apply. A natural person shall notify the tax authority of any circumstances related to changing his or her residency for tax purposes and complete the form for determining residency for tax purposes.
Taxable income
There is no exhaustive list of items of income. Therefore, all income received by a resident is subject to income tax. Any compensation for certified expenses incurred for the benefit of another person and any compensation for direct proprietary damage shall not be deemed to be income of a natural person, except for compensation paid in connection with business. Categorisation of income as earned income or income from capital has no substantive meaning for income tax purposes given the flat tax rate.
Exempt income
Most important types of exempt earned income are:
1) scholarships and grants paid pursuant to law or from the state budget, and benefits paid pursuant to law;
2) maintenance support and maintenance allowance received pursuant to the law;
3) compensation for expenses related to business travel and daily allowances during assignments abroad;
4) compensation for employment related use of a personal car.
Exempt income from capital
Income tax is not charged on:
1) accepted estate;
2) income from the transfer of movable in personal use;
3) income from the exchange of a holding in the course of a merger, division or transformation of companies;
4) gains from the transfer of immovable property if an essential part of the immovable is a dwelling which was used by the taxpayer as his or her place of residence until transfer (tax exemption is not applied to more than one transfer within two years).
Employment income
Income tax is charged on all amounts paid to an employee, including wages and salaries, additional remuneration, additional payments. Income tax is charged on all fees paid to a natural person on the basis of a contract for services, authorisation agreement or any other contract under the law of obligations. Directors’ fees and other remuneration are taxed analogously.
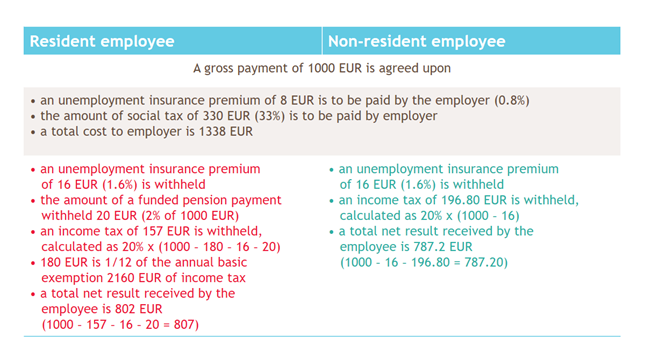
See examples of tax calculations for wages of a resident and non-resident employee.
Professional (business) income
Business is a person's independent economic or professional, the aim of which is to derive income from the production, sale or intermediation of goods, the provision of services, or other activities, including creative or scientific activity. Transfer of securities owned by a natural person does not constitute business. Sole proprietors entered in the commercial register may make the deductions from their business income in accordance with Income Tax Act. Deductions relating to enterprise shall be made from the business income of the period of taxation of a sole proprietor and the received amount shall be divided by 1.33 (social security tax) before it is multiplied by the tax rate.
Dividends
Income tax is charged on all dividends and other profit distributions received by a resident natural person from a foreign legal person in monetary or non-monetary form. Income tax shall not be charged on dividends if income tax has been paid on the share of profit on the basis of which the dividends are paid or if income tax on the dividends has been withheld in a foreign state.
Investment account
Income tax liability arising from gains or income received on particular financial assets can be postponed upon compliance with the conditions provided for in Income Tax Act. In order to defer income tax liability financial assets must be acquired exclusively for the funds on a cash (investment) account opened for such purpose with a credit institution or and any income received on financial assets shall be immediately transferred to the investment account.
Interest
Income tax is charged on all interest accrued from loans, securities, leases, deposits and other debt obligations, including such amount calculated on the basis of the debt obligations by which the initial debt obligations are increased. The fine for delay (late interest) payable in the event of delay in performance of a monetary obligation is not deemed to be interest. Income tax is not charged on interest received from deposits with a credit institution which is a resident of a Contracting State or through or on account of a permanent establishment of a credit institution located in a Contracting State.
Capital gains
Income tax is charged on gains from the sale or exchange of any transferable and monetarily appraisable objects, including real or movable property, securities, registered shares, contributions made to a general or limited partnership or an association, units of investment funds, rights of claim, rights of pre-emption, rights of superficies, usufructs, personal rights of use, rights of commercial lessees, redemption obligations, mortgages, commercial pledges, registered securities over movables, or other restricted real rights, or the ranking thereof, or other proprietary rights. A resident natural person has the right to deduct any loss suffered upon the transfer of securities during a period of taxation from the gains derived from the transfer of securities during the same period of taxation. As regards exempt income from capital, see above.
Basic exemption
The basic exemption deductible from the income of a resident natural person during a period of taxation is 2160 euros (1/12 per calendar month).
Housing loan interests
A resident natural person has the right to deduct interest payments made during a period of taxation to a credit institution which is a resident of a Contracting State, a financial institution belonging to the same group with such company or branch of a non-resident credit institution registered in a Contracting State for a loan or finance lease taken in order to acquire a house or apartment for himself or herself from the income which he or she receives during the period of taxation. Interest payments for a loan or lease taken in order to acquire a plot of land in order to build a house may be deducted from income under the same conditions.
Training expenses
A resident natural person has the right to deduct the training expenses of himself or herself or a relative in descending line, sister or brother of less than 26 years of age or, if no such training expenses are incurred, the training expenses of one permanent resident of Estonia of less than 26 years of age, from the income which the resident natural person receives during the period of taxation.
Gifts and donations
A resident natural person has the right to deduct certified gifts and donations which are made during a period of taxation to specified non-profit associations from the income for the period of taxation.
Insurance premiums and pension fund units
A resident natural person has the right to deduct from the income received during a period of taxation insurance premiums paid to an insurance undertaking holding an authorisation issued by a Contracting State and amounts paid to acquire units of a voluntary pension fund established in Estonia or a voluntary pension fund operating in a Contracting State.
Mandatory social security contributions
Contributions to a mandatory funded pension are deducted from the income of a resident natural person during a period of taxation.
Limitations on deductions
Deductible amount of housing loan interests, training expenses, gifts and donations altogether is set to 1200 euros per taxpayer during a period of taxation, and to not more than 50 per cent of the taxpayer's income taxable in Estonia for the same period of taxation.
Income from foreign states
If a resident natural person received at least 75 per cent of taxable income in a foreign state during a period of taxation and part of the income received in the foreign state is exempt from income tax in Estonia, the person can make the deductions from income taxable in Estonia in proportion to its share in his or her taxable income for the period of taxation.
Losses
If the total amount of the expenses allowed exceeds the business income derived by a taxpayer (sole proprietor) during a period of taxation, the amount by which expenses exceed business income may be deducted from business income during up to seven subsequent periods of taxation. Expenses which have been carried forward for more than seven years shall not be carried forward to subsequent periods of taxation.
Taxable period
The period of taxation for a natural person is one calendar year.
Tax rate
Flat tax rate 21%.
Withholding taxes
Income tax is withheld from:
1) salaries, wages and other remuneration subject to income tax paid to a resident natural person and remuneration paid to members of the management and controlling bodies of a legal person;
2) remuneration or service fees paid to a natural person on the basis of a contract for services, authorisation agreement or any other contract under the law of obligations;
3) interest payment subject to income tax paid to a resident natural person;
4) rent from a commercial or residential lease or payment for encumbering a thing with limited real rights, paid to a resident natural person, and royalties paid to a resident natural person;
5) other payments of taxable income made to a resident natural person, except capital gains which are subject to taxation by way of self-assessment.
Tax return
A resident natural person is required to submit an income tax return to the Tax and Customs Board concerning the income of a period of taxation not later than by 31 March of the year following the period of taxation. It is possible to submit an income tax return through the e-service of the Tax and Customs Board as of 15 February of the year following the period of taxation.
Pre-completed data
The Tax and Customs Board shall complete the income tax return concerning the income of a resident natural person during a period of taxation and the deductions and concerning the transfer of the particular securities on the basis of the data at the disposal of the Tax and Customs Board and make the pre-completed tax return available to the taxpayer through the e-service of the Tax and Customs Board and at the service point of the Tax and Customs Board as of 15 February of the year following the period of taxation.
Payment of tax
The Tax and Customs Board shall calculate any additional amount of tax due (additional amount due) and issue a written tax notice to this effect to the taxpayer. A taxpayer is required to pay any additional amount due which is specified in the tax notice into the bank account of the Tax and Customs Board not later than by 1 July of the calendar year following the period of taxation.
Non-resident
A non-resident shall pay income tax only on income derived from Estonian sources (limited tax liability). The list of items of taxable income for non-residents provided for in Income Tax Act is exhaustive. The main items of taxable income are:
1) income from work performed in Estonia if the payment was made by an Estonian resident or a non-resident operating in Estonia as an employer or a permanent establishment located in Estonia, or if the person has stayed in Estonia for the purpose of employment for at least 183 days over the course of 12 consecutive calendar months;
2) remuneration paid by a resident legal person to a non-resident member of a management or controlling body or by a permanent establishment located in Estonia to a non-resident member of a management body of the permanent establishment for the performance of functions;
3) business income derived by a non-resident in Estonia;
4) gains derived by a non-resident from a transfer of property if the immovable is located in Estonia;
5) income derived by a non-resident from a commercial lease or royalties if the immovable is located in Estonia;
6) remuneration paid to a non-resident artist or athlete in connection with his or her performance or competition in Estonia or the presentation of his or her works in Estonia.
See examples of tax calculations for wages of a resident and non-resident employee.
Non-resident’s exempt income from capital
Income tax is not charged on the following income of a non-resident (main items):
1) accepted estate;
2) income from sale of movable in personal use;
3) gains from transfer of immovable if an essential part of the immovable is a dwelling which was used by the taxpayer as his or her place of residence until transfer (tax exemption is not applied to more than one transfer in two years).
Estonian sourced income
A natural person who is a resident of a Contracting State and who received at least 75 per cent of his or her taxable income in Estonia during a period of taxation can make the deductions from income taxable in Estonia in proportion to its share in his or her taxable income for the period of taxation.
Tax return of non-resident
A non-resident is required to submit an income tax return concerning the gains derived during the calendar year and subject to taxation to the Tax and Customs Board not later than by 31 March of the following year. The same applies to other items of income received by non-resident from which income tax has not been withheld.
In the case of transfer of an immovable, the income tax return shall be submitted after receiving the gains. If payments for a transferred immovable are made by instalment, a tax return concerning the agreed transaction price is also submitted within one month after receiving the first instalment.
Examples of tax calculations for wages of a resident and non-resident employee (2017):